The Big Bang :
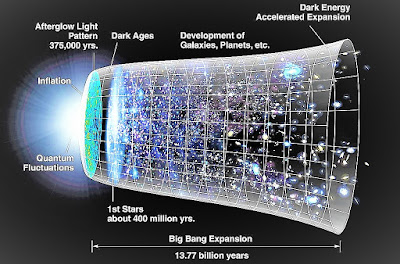
Lets start from about 14 billion years ago, the Universe materialized out of nothing for unknown reasons. Infinitely smaller than an atom to begin with, the Universe expanded to a trillion kilometers across in under a second - an event called The Big Bang.
Time came into existence when the Universe began, so the question arises "what happened before?" has no meaning. Space also came into existence. The Big Bang was not an explosion of matter through space but it was an expansion of space itself.
At first the Universe consisted of pure energy, but within a trillionth of a second some of this energy turned into matter, forming a vast soup of subatomic particles (particles smaller than atoms). It took nearly about 400,000 years for the particles to cool down enough to form atoms, and then another 300 million years before the atoms formed planets, stars, and galaxies. The expansion that began in the Big Bang continues to this day, and most scientists think it will carry on forever.
The Universe began as something called a singularity: a point of zero size but infinite density.
Discovery of the Big Bang
The first scientific evidence for the Big Bang was found in 1929, when astronomers discovered that light from distant galaxies in reddened. This colour change happens when objects are moving away from us, making light waves stretch out and change colour. The more distant the galaxies are, the faster they are rushing away. This shows that the whole Universe is expanding.
More evidence of the Big Bang came in the 1960s, when astronomers detected faint microwave radiation coming from every point in the sky. The mysterious energy is the faded remains of the intense burst of energy released in the Big Bang.
Formation of Universe:
let us discuss the formation of our Universe in 10 main steps:
- The Universe appears out of nowhere. At the start, the Universe consists purely of energy and is infinitely dense and unimaginably hot - 10 billion trillion trillion degree Celsius.
- Within a tiny fraction of a second, the Universe balloons in size from trillions of times smaller than an atom to the size of a city. The rate of expansion then slows.
- The intense energy of the newborn Universe creates matter. At first, the matter is a soup of particles and antiparticles. These crash into and cancel each other out, turning back into energy. But some of the matter is left over - this will eventually turn into atoms and later stars and galaxies.
- After 379,000 years, the Universe cools enough for atoms to form. The Universe is now a vast cloud of hydrogen and helium. Light can now pass through space more easily, and the Universe becomes transparent.
- Half a million years after the Big Bang, matter is spread out almost evenly in the Universe, but tiny ripples exist. Working on these denser patches, gravity begins pulling the matter into clumps.
- After 300 million years, stars appear. Stars from when great clouds of gas are pulled into tight knots by gravity. The pressure and heat become so intense in the dense pockets of gas that nuclear reactions begin, igniting the star.
- After 500 million years, the first galaxies are forming. Galaxies are enormous clouds of stars, held together by gravity.
- Now after about 5 billion years, the Universe consists of vast clusters of galaxies arranged in threads. Also after 8 billion years, the expansion of the Universe begins to accelerate. Check out the article of ours about Expanding of Universe.
- Our Solar System forms after about 9 billion years. When the Universe is 20 billion years old, the Sun will expand in size and destroy Earth.
- The Universe will carry on expanding forever, becoming cold and dark everywhere.





0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.
Emoji